Whether you are just getting into photography or have been shooting for a while, you have probably heard the term “crop factor”. With so many different cameras and camera systems available today, this particular term comes up very often in product specifications, marketing materials, articles, books and you might even hear it in conversations between photographers. If you do not know what it really means or want to get a better understanding of crop factor, this article will hopefully make it easier for you to understand it better. Please keep in mind that this article was written for beginners, so many of the terms and explanations are over-simplified.
Table of Contents
Background
Before digital, 35mm film was a reference format due to its mass adoption and popularity. If one used a 50mm lens on an SLR film camera, everyone knew exactly what it looked like in terms of field of view and the resulting image, so understanding and discussing different lenses and focal lengths was easy. Due to technological challenges and high manufacturing costs, making digital camera sensor sizes that matched the size of 35mm film was impractical, so camera manufacturers started out with smaller sensors in digital SLR cameras (see this article to understand how a DSLR works). Allowing for a smooth transition from film to digital meant keeping the camera mounts and lenses the same so that those who were already invested in a camera system could simply replace their film camera bodies without having to worry about repurchasing lenses and accessories.
But using a smaller sensor than 35mm film created a new problem – both field of view and captured images appeared narrower, because the corners of the image frame were getting “cropped”, or chopped off. To understand what happens in the camera with a smaller sensor, take a look at the below illustration:
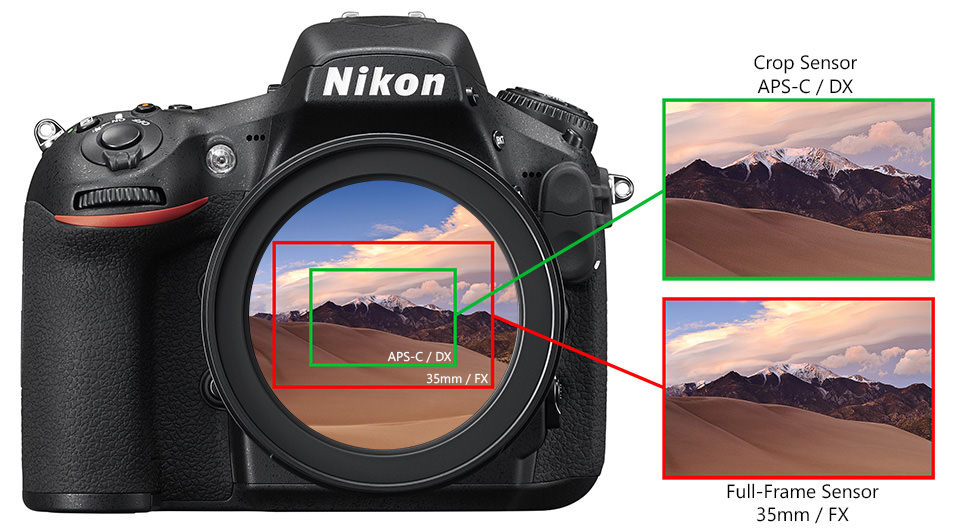
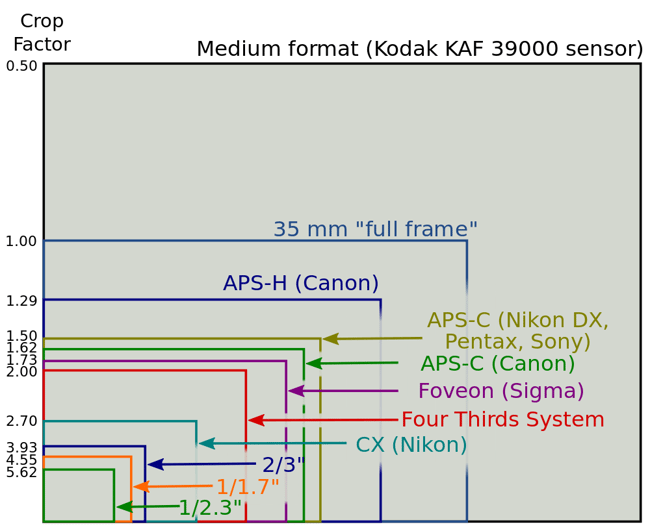
As you can see, lenses project a circular image (usually referred to as “image circle”), but the sensor only records a rectangular portion of the scene – the rest of the image is thrown away. If the sensor covers the full area of the image circle, it is called a “full-frame sensor” and if it covers a smaller portion that throws away or crops part of the image, it is called a “crop sensor”. Full-frame sensors have the same physical size as 35mm film (36mm x 24mm), while crop sensors are smaller and can vary in size depending on the system and manufacturer. Here is a great illustration of various sensor sizes, courtesy of Wikipedia:
Although “full-frame” and “crop sensor” are fairly common names for digital camera sensors, some manufacturers refer to cameras and sensors differently. For example, Nikon often refers to its full-frame cameras as “FX” and their crop sensor cameras as “DX”, while others refer to cameras by sensor size, such as “35mm” and “APS-C”.
For now, all this nomenclature does not matter – look again at the first image and see the resulting photographs on the right side of the camera. Notice that the two images look drastically different. The image captured with the smaller crop sensor looks narrower, or more “zoomed in”, while the image captured with the full-frame sensor appears wider. This is the problem I referred to earlier – although the lens and its focal length might be the same, capturing the same scene with a smaller sensor than full-frame / 35mm film will yield a different, narrower field of view.
A good analogy to understand this effect is using a real photograph. If you take an 8×10 photograph and use scissors to cut out the edges of the photo to make it a 6×8, you are essentially doing the same thing as a crop sensor. However, there is one caveat here – sensor resolution, which can make the image appear more magnified. Don’t worry about this for now, as I will explain this in more detail further down below.
What is Crop Factor?
Now that you know what happens to the field of view and the resulting image when using cameras with different sensor sizes, let’s talk about the crop factor. What is it and what does it do? To make it easier for photographers to understand what the field of view of a lens will look like when compared to a 35mm film or full-frame camera, manufacturers came up with an easy way to calculate the “equivalent” focal length of a lens. Since the corners of the image are cropped and thrown away, a wide-angle lens is obviously not as wide anymore, while a telephoto lens makes things appear closer. “Crop factor” is the ratio of the sensor size to 35mm / full-frame (see below). You take the provided crop factor number, multiply it with the focal length of the lens and you get the equivalent focal length relative to 35mm film / full-frame.
For example, Nikon’s “DX” cameras have a crop factor of 1.5x, so if you take a 24mm wide-angle lens and multiply it by this number, the result is 36mm. This basically means that the 24mm lens on the crop sensor DX camera would behave more like a 36mm lens on a full-frame camera in terms of field of view. In essence, if you mounted a 24mm lens on this crop sensor camera, then mounted a 36mm lens on a full-frame camera, put them side by side and took pictures of the same subject at the same distance, both would yield a very similar field of view. However, this does not mean that the resulting images would look identical – changing focal length or camera to subject distance can have a drastic effect on perspective, depth of field and background blur, but that’s another topic that we are not yet ready to discuss.
Here is a sample list of current cameras that have different crop factors:
- 1.5x Crop Factor: Nikon DX (Coolpix A, D3300, D5500, D7100); Pentax K-5 II; Sony A5100, A6000; Samsung NX1; Fuji X-A1, X-M1, X-E2, X-T1, X-Pro1
- 1.6x Crop Factor: Canon Digital Rebel, 70D, 7D Mk II, EOS M2
- 2.0x Crop Factor / Micro Four Thirds: Olympus OM-D Series; Panasonic DMC Series
- 2.7x Crop Factor: Nikon CX (J4, S2, AW1, V3); Sony RX100 III, RX 10; Samsung NX Mini
How Crop Factor is Calculated
The math to derive the crop factor is quite simple. Knowing the physical size of the sensor, you first calculate the diagonal using Pythagorean Theorem (a² + b² = c²), then divide the number by the diagonal of the crop sensor. Here is an example on how to derive the crop factor of the Nikon CX sensor:
- 35mm / Full-frame diagonal: 36² + 24² = 1872, so the diagonal is 43.27 (√1872)
- Nikon CX sensor diagonal: 13.20² + 8.80² = 251.68, so the diagonal is 15.86 (√251.68)
- Crop Factor: 43.27 / 15.86 = 2.73
So we can see that the crop factor of the Nikon CX sensor is 2.73x, which usually just gets rounded to 2.7x.
Common Crop Factors and Equivalent Focal Lengths
And now let’s take a look at the common focal lengths and crop factors, along with resulting equivalent focal lengths:
| 35mm | 1.5x | 1.6x | 2.0x | 2.7x |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14mm | 21mm | 22.4mm | 28mm | 37.8mm |
| 18mm | 27mm | 28.8mm | 36mm | 48.6mm |
| 24mm | 36mm | 38.4mm | 48mm | 64.8mm |
| 35mm | 52.5mm | 56mm | 70mm | 94.5mm |
| 50mm | 75mm | 80mm | 100mm | 135mm |
| 85mm | 127.5mm | 136mm | 170mm | 229.5mm |
| 105mm | 157.5mm | 168mm | 210mm | 283.5mm |
| 200mm | 300mm | 320mm | 400mm | 540mm |
As you can see, the size of the sensor and its crop factor can have a drastic effect on the equivalent focal length of a lens. A 200mm lens on a small sensor with a 2.7x multiplication factor (Nikon’s CX cameras) produces an equivalent focal length of 540mm!
Equivalent Focal Length
Sadly, this is where things can get confusing for many photographers. The focal length of a lens is the physical property of a lens and it never changes irrespective of the camera sensor. So when you look at the above table, always keep in mind that the smaller sensor is not magically transforming your lens into a longer lens – it is just cropping a lot of the image, as shown in the below illustration:
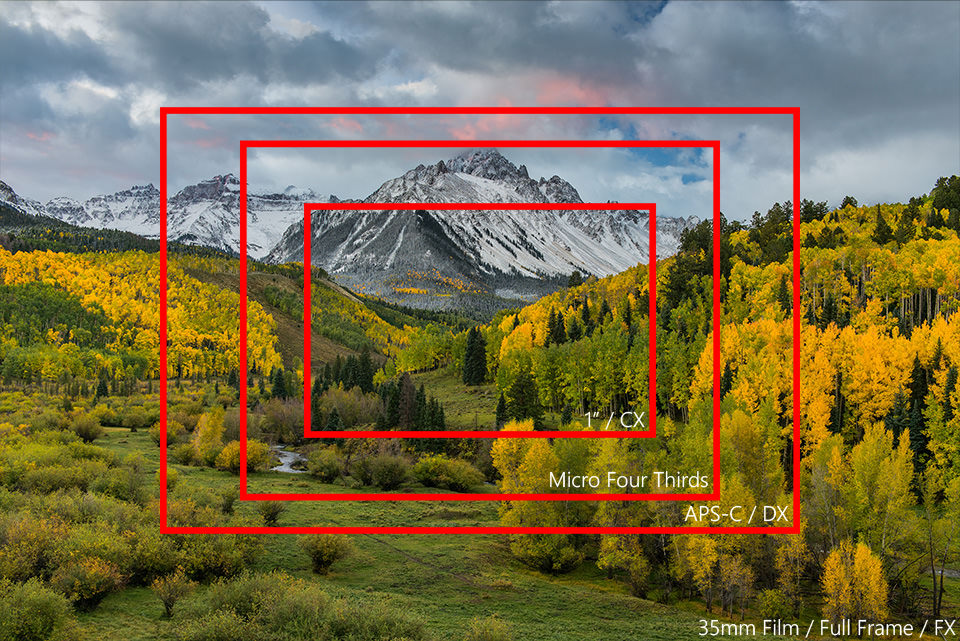
Lens Size / System Size
Now take another look at the first image in this article and the above image and note just how much of the photograph is getting chopped off. Manufacturers quickly realized that there were advantages to using smaller sensors. Since edges of the image circle were not being used, they could make smaller lenses that used less glass, allowing for more compact and lightweight lens design. Why waste all that space? This gave birth to smaller and lighter lenses first, then as technology progressed, new generation “mirrorless” cameras were born that were specifically made with crop sensors and smaller lenses to be compact and lightweight.
Today, when evaluating DSLR lenses, you will often come across lenses that are made specifically for crop sensor cameras. Since these lenses have a smaller image circle, they will either not work at all on full-frame cameras, or will work (provided that they have the same lens mount, as shown below), but display very dark corners, as shown below:
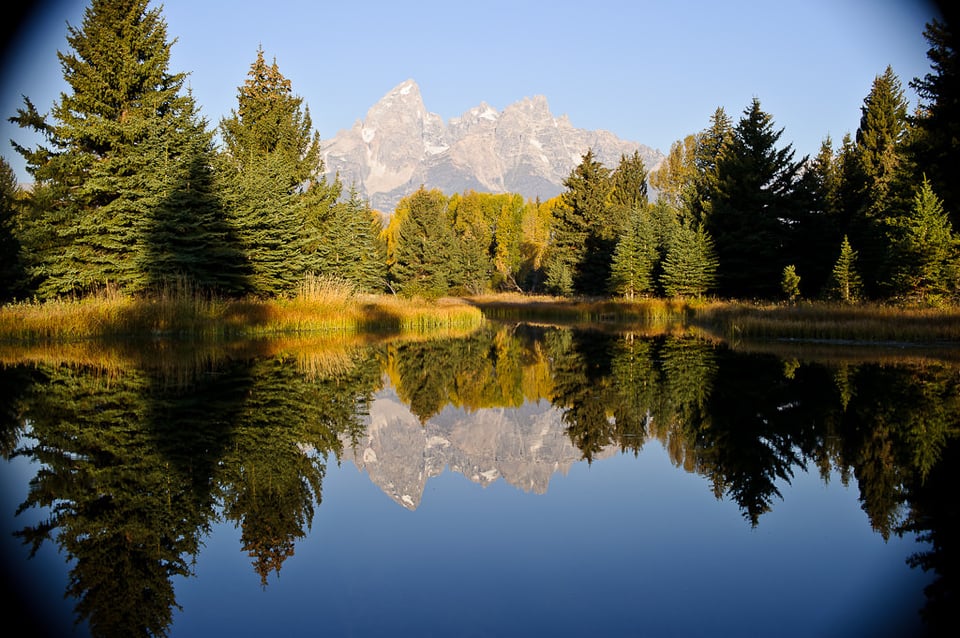

To make it easier for potential buyers to distinguish between lenses specifically designed for crop sensors, manufacturers came up with different abbreviations that are added to lens names. Here is a list of abbreviations for crop sensor lenses from different lens manufacturers:
- Nikon: DX
- Canon: EF-S, EF-M
- Sony / Konica Minolta: DT, E
- Pentax: DA
- Samsung: NX
- Sigma: DC
- Tamron: Di II
- Tokina: DX
For example, if you look at a Nikon lens and see “DX” on its label, it indicates that the lens is designed to be used only on crop sensor Nikon DX cameras, while Canon lenses will clearly specify “EF-S” for theirs.
Same Mount, Different Lenses
Keep in mind that some lenses are specifically made to be used on crop sensor cameras, while standard full-frame / older 35mm film cameras will work on both crop-sensor and full-frame cameras. It is fairly common to see a manufacturer with the same mount size, but with lenses that are designed for different sizes. For example, Nikon’s F mount will allow mounting both full-frame and DX lenses. The same goes for Sony mirrorless cameras, which have the same Sony E mount, but could have lenses designed specifically for crop sensor Sony cameras like Sony A6000, or full-frame lenses that will work on both. Here is the new Sony A7 II compared to the Sony A6000:

As you can see, both have the same E-mount, but the differences in sensor size are obvious. When purchasing lenses for the A7 II, you will have to buy full-frame “FE” lenses, while for the A6000 you will be able to use both FE / full-frame lenses and regular E series lenses with smaller image circle.
It is important to understand that the best lenses for digital cameras are usually full-frame lenses (with a few exceptions), which is why they are often pricier and tend to retain value better over time than their smaller counterparts. Unfortunately, neither Nikon nor Canon have been eager to produce very high-quality lenses for their crop sensor cameras – both only have a couple of professional-level lenses and the rest of the line is mostly comprised of slow zoom lenses…
Sensor Size vs Resolution
Remember the 8×10 printed photo I talked about above? It is true that taking scissors and cutting the edges of the frame to yield a 6×8 photo is similar to what a crop sensor does. However, there is one important factor that we should not forget about – sensor resolution. Since each digital camera sensor is comprised of millions of pixels, using a smaller sensor should translate to fewer pixels right? Not really. If the sensor is made with physically smaller pixels, two sensors could potentially have the same resolution (in some cases, a crop sensor could actually have more pixels than a full-frame sensor).
For example, the Nikon D4 has 16 million pixels on its full-frame sensor measuring 36.0 x 23.9mm, while the Nikon D7000 also has 16 million pixels on its 23.6 x 15.6mm sensor. With such a drastic difference in sensor size but having the same number of pixels, the difference between the two is the physical size of each pixel. The Nikon D4s has much bigger pixels measuring 7.3µm, while the D7000 pixels are much smaller at 4.78µm, so those pixels are basically packed closer together. Since smaller pixels translate to more noise and less dynamic range in images, the Nikon D7000 in this case simply cannot match the image quality of the Nikon D4 in low-light situations. That’s why manufacturers are so keen on talking about megapixels, rather than sensor sizes! They want you to pay attention to the fancy megapixel number and they do not want to mention how small the sensor actually is. Your phone camera might have the same resolution as your DSLR, but it sure does not mean that the two will produce the same quality images.
At the same time, modern crop sensors have gotten very good at handling noise, especially at low to medium ISO levels. In good light, you will have a hard time seeing differences in image quality between full-frame and 1.5-1.6x crop sensors. So there are certainly advantages to crop sensor cameras here. Smaller pixels do quite well in good light, so if two sensors of different sizes but the same resolution perform similarly in daylight, then the camera with a smaller sensor could actually be advantageous for getting closer to the action. Although the image is still getting cropped, it is being magnified at the same time! If we go back to the 8×10 printed photo example, imagine cutting the corners of the photo to yield a 6×8, but then taking that 6×8 and enlarging it to another 8×10 photo (say by scanning and reprinting) – that’s basically what’s going on here.
Sports and wildlife photographers might prefer such a setup, because their long lenses would give them more “reach” when used on crop sensor cameras. For example, a 300mm lens on a crop sensor camera is equivalent to a 450mm lens on 35mm / full-frame camera in terms of field of view. If low-light performance is not critical, that’s a pretty big gain in reach, which is certainly an advantage. That’s obviously assuming that the lens being used is actually capable of resolving that much detail. Some older lenses not designed for high-resolution sensors might not be able to resolve enough detail and hence would not necessarily translate to better reach…
If you would like to see the advantages and disadvantages of crop sensor cameras, please see my Nikon DX vs FX article. And if you are ready for a much longer and detailed article explaining all of the above at a higher level, please see my article on Equivalence.
Hope this article clarifies the subject of Crop Factor. Don’t let all the technicalities get in your way though – learn to use the gear you have effectively and focus on taking better pictures. Remember, most modern cameras are amazing, so the barrier to professional-quality pictures is you, not your gear…
Thank you for this article. Not only did I enjoy reading it, I also learned alot.
Superb article explaining the mechanics of crop sensors in easily understandable language
good evening . i read this article.. it is awesome… with lot of information. Today i understood well regarding cropfactor and how to calculate the actual focal lenth of the lens. thanks for clearing the need of many pohotographers.. i wish u a happy, health and peaceful life. take care
WITH REGARDS… SHANKAR RAPARTHI, CIVIL ENGINEER , HYDERABAD, INDIA.
Excellent article! It was clearly explained. Now I understand! Thanks!
So if I buy a lens for APS camera, the focal lenghts are true to what I see? I dont need any conversion? For ex, if I buy the sony 16-50mm zoom lens, what I see through the lens is a range of 16-50? Thanks!
This is a great article. On a Nikon Z system FB group, there’s a debate raging about this. Some people are suggesting that the focal length of a lens designed for crop sensors does not need to be multiplied x1.5 to work out the effective focal length.
So for example, the Sigma Art 18-35mm 1.8 DX lens is 18-35mm on a DX body (as opposed to x1.5 = effective focal length of 27-52mm). But you said:
“The focal length of a lens is the physical property of a lens and it never changes irrespective of the camera sensor. ”
So from this we know that regardless of what sensor size the lens was designed for, you always work out the effective focal length of a lens when using it on a crop sensor right?
It’s not the focal length that is being “changed” on lenses made for DX (e.g. so that an 18mm image on DX lens and body will look the same as an 18mm image on an FX lens and body), but rather the amount of glass to enable them to be cheaper and more compact, because as you say, you don’t need as much glass to cover a smaller sensor. Have I understood this correctly?
36^2+24^2=1872 (not 1872^2)
I wrote what I wrote because the square root of 1872 is not an easy number to illustrate. I updated the article with something that hopefully makes more sense now.
Article was too good.
Thanks a lot to describe the things in a very wonderful manner.
Since medium film (1901) format predates 35mm film (1934), the 35mm is the CROP SENSOR when we use the medium format as the reference.
This whole crop factor conversation becomes stupid since a medium format sensor is NOT CROPPING anything.
Nasim,
Thanks for a great article. I am just getting into photography so pardon me if my question seems too “juvenile”.
What is the exact significance of a crop factor ?
Can cameras be rated according the the crop factor ? Which cameras are considered better ? Cameras with large crop factor or small ?
Which cameras are best for macro photography ?
Thanks.