Below is the easiest and quickest way to test if your DSLR has an autofocus issue, along with a recommendation on what to do if there is a problem. This test can be used to detect front or back focus issues with a particular lens or a camera body. I will be using the Nikon D800E as a reference camera for this article, but any modern DSLR with Live View capability can be used for the same test (even entry-level DSLRs such as the Nikon D3500 have a Live View mode). Why would you want to test your camera for autofocus issues? Because if your camera or your lenses are defective or have a calibration problem, then you will not be able to obtain critically sharp images.
Table of Contents
1) What You Will Need
For this test, you will need the following:
- Any DSLR with Live View mode capability.
- At least one lens, but preferably 2-3 lenses if you want to isolate the problem to the camera or your lenses.
- A good stable tripod.
- A flat vertical surface in a very brightly lit area. For example, your garage door or a wall inside your home that is adjacent to a very large window will do fine.
- Print out either this Siemens Star Focus Chart or this Focus Test Chart on regular letter size paper. You can print it on a laser printer or inkjet (doesn’t really matter). Make sure to print on regular paper, not anything glossy like photo paper.
- Scotch tape or some other adhesive material to keep the focus chart on the wall.
2) Set Up
The setup process is pretty straightforward, as explained in detail below:
- Pick a spot on your wall where you will hang the focus chart. The wall must be vertical and straight. You want the focus chart to be right across from the camera, so do not hang it too high or too low.
- Once the focus chart is up, set up the camera on your tripod and make sure that the camera is placed parallel to the focus chart. Make sure that the camera is not tilted left / right / up / down – it must be parallel to the wall. To check if your level is good, look from the side and make sure that the lens is pointing directly at the center of the focus chart. Here is how I placed my setup:

Please note that I captured the image above the camera to show where the focus chart is relative to the camera. The focus chart is located right across from the camera. - The distance between the camera and the wall depends on the focal length of the lens you are testing. If you are using a 50mm f/1.4 lens, then the distance between the camera and the test chart should be approximately 5 to 7 feet (1.5-2 meters). If you are using a wide-angle lens, then stand closer and if you are using a telephoto lens stand further away. The goal is to stand close enough to be able to have a shallow depth of field. The chart should take about 1/3-1/4 the size of the entire image, as shown below:
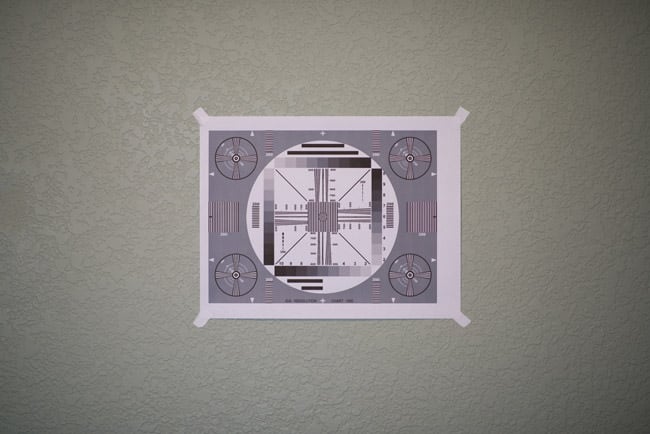

- You are all set, now it is time to take some pictures
3) Camera Setup
When testing the autofocus accuracy of a camera or lens, it is always best to have exposure consistency. Therefore, I recommend switching to Manual mode and keeping the same exposure for each shot. Here is a summary of what I would recommend in terms of camera setup:
- Switch your camera to full Manual Mode.
- Set your lens aperture to maximum aperture. For example, if you have a Nikon 50mm f/1.8G lens, set your aperture to f/1.8.
- Set your ISO to base value such as ISO 100.
- Use the exposure meter inside the camera to determine the optimal shutter speed. Take sample shots and make sure that you can see the chart clearly. Ideally, your shutter speed should be pretty fast at something like 1/500 of a second. If you are getting really slow shutter speeds like 1/10, then it means that you do not have sufficient ambient light. Either take the setup outside and do it in bright light or add more light to illuminate the focus chart. If the amount of ambient light is insufficient, your test will be flawed. It is extremely important to make sure that you are doing this in a well-lit environment since the Phase Detect sensor on the camera needs plenty of light.
- Make sure that AF Fine Tune/AF Micro Adjustment is turned OFF if your camera has it. On the Nikon D800, for example, you go to Setup Menu->AF fine tune->AF fine-tune (On/Off)->OFF.
- Set the focus point to the center focus point. The center focus point is always a cross-type sensor, so it is the most accurate in your camera.
- Turn off any sort of lens corrections in your camera (vignetting, distortion, chromatic aberration, etc.). You do not want anything to potentially influence the test results.
- Set the camera to AF-S/Single Servo mode.
- While this test should work for both JPEG and RAW images, cameras add extra sharpening, colors, etc to JPEG images. Therefore, I would recommend capturing test data in RAW format.
- Set your camera Live View mode to “Tripod” (if you have such a setting).
- If your camera has a Mirror Lock-Up feature and you have a remote camera release, you can use those to prevent camera shake (can be very useful if your shutter speed is slow).
4) Capture
Now that you have everything set up, it is time to capture some data. Make sure to follow the below steps carefully, otherwise, you might invalidate your test results:
- First, you will capture the focus chart in Live View mode. This will be your “reference” shot. Once you turn Live View mode on, zoom in to the center of the focus chart and either half-press the shutter or press the AF-ON button on the back of the camera to force it to focus the lens. Go ahead and press the shutter button now and capture the image. Now analyze the image at 100% view and make sure that it is tack sharp in the center where the focus point is. If it looks sharp, you did everything right. If it looks blurry, then your camera did not acquire focus properly in live view mode. Repeat until you get a sharp image. Only keep one image that is sharp and delete the rest.
- The second image will be captured without Live View. Turn off Live View mode. Now look through the viewfinder and rotate the focus ring on the lens until the focus chart looks completely out of focus. We want to force the camera to reacquire focus. Now half-press the shutter button or press the AF-ON on the back of the camera to acquire focus and wait until you see a green mark inside the viewfinder or the camera beeps (if you have beep turned on), confirming that focus is acquired. Take a shot. Again, rack the focus by rotating the focus ring until everything is out of focus and repeat the process. Ideally, you should capture at least 3 shots this way, since you need to eliminate any possibility of a potential autofocus error.
Before we analyze the captured data, let me explain exactly what you are doing here. First, you captured an image in Live View mode, then you captured an image normally, as you would if you were taking pictures. Why are we doing this? All DSLR cameras rely on a “Phase Detect” autofocus sensor located inside the camera (see my article on phase detection autofocus). The good news is that the Phase Detect system is very fast. The bad news is that the Phase Detect sensor itself and lenses must be properly aligned and calibrated for this system to work. And that’s exactly what we are trying to test here. When using Live View mode, the mirror inside the camera flips up and the Phase Detect sensor can no longer be used to acquire focus. Therefore, the camera relies on a different focus method called “Contrast Detect” to acquire focus. The camera forces the lens to focus back and forth until the image looks sharp, which is why this method is very slow in comparison. However, because focus confirmation happens electronically through the camera sensor, it will always be accurate. That’s why we are using the first shot captured through Live View as a reference image.
5) Analyze the Data
Now that we have a sharp reference image, along with a bunch of other images, it is time to analyze the data. Import your images into your computer with whatever post-processing tool you use. Open up the very first image and make sure that it looks sharp in the center. Here is a crop of my reference shot that I captured with the Nikon 24mm f/1.8G lens:
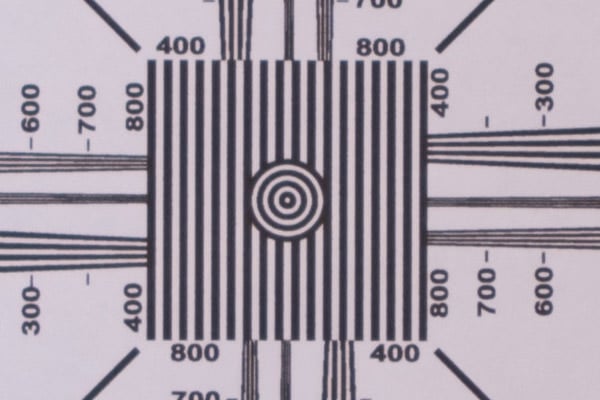
The image looks good and sharp. Please note that this is a RAW image without any kind of sharpening applied to it.
Now, take a look at the other 3-4 images you captured after this one. Do they look more or less the same? Or do they all look out of focus? Here is a second shot that I captured, which clearly indicates a focus problem:
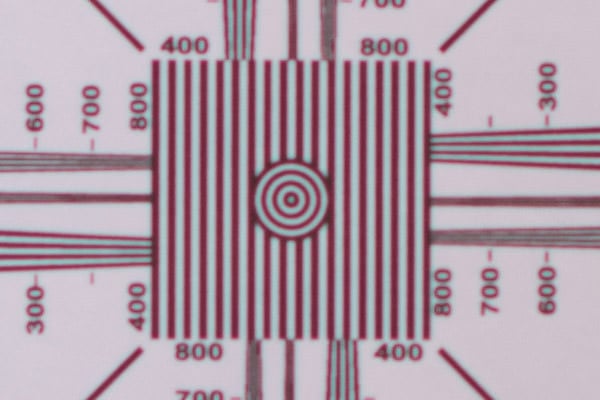
As you can see, the image not only looks out of focus, but we are also seeing some aberration problems in the image as well (a pretty normal thing to see when an image is out of focus). All three shots were very similar, which clearly indicates a focus problem either on the lens or the camera body.
It is critical to view images at 100% view and go back and forth between the reference image and the other shots to compare. If things look out of focus, repeat the whole thing again to confirm that you are indeed seeing a focus problem. You should either be getting consistently good results or consistently bad results. If the results are consistently good and images look good shot to shot, then you do not have a focus issue. You can stop doing tests at this point and breathe – you are in good shape. If you are getting consistently bad results, then the next step is to find out whether it is your lens or the camera body that has an autofocus problem.
6) Is It The Camera or the Lens?
As I have already pointed out, it is best to test multiple lenses when assessing the autofocus accuracy of your camera. If you only have one lens to test, then it would be impossible to tell whether the lens or the camera have alignment issues. Sometimes it could be both. If you have 3-4 different lenses, perform the above test on all lenses you have and see what you get. If all lenses show very similar results, then your camera is most likely to blame for AF issues. Still, it will be hard to pinpoint the exact source of the problem, because it all depends on how badly calibrated your lenses were before you started the test. See my article on lens calibration.
I have been shooting with a number of different Nikon DSLRs during the last 6 years and none of them had a focus problem with most of my lenses. I tested 2 samples of the Nikon D800 and both were perfect, with no signs of focus problems. However, the Nikon D800E that I recently received clearly has a misaligned phase detect sensor, because none of my lenses can accurately focus with it. Dialing -20 in AF Fine Tune seems to be fine with some lenses, but clearly not enough for others, so the camera has a severe case of backfocus. Hence, I was able to isolate the problem to the camera. Interestingly, I also recently added another Nikon 14-24mm f/2.8G lens, which has a really bad front focus problem. When I use it on my Nikon D700, the focus is completely off and I have to dial +20 to get anything in reasonable focus. Guess what – when I mount it on the Nikon D800E, it focuses perfectly because the focusing misalignment on both pretty much cancels each other out. So you have to be careful when trying to determine the source of the problem.
7) What to Do if There is a Focus Issue
So what do you do if you find a focus issue with your camera? Most people would take their camera or lens back to the place where they bought it from. While the return policy is created for this purpose, I would actually recommend NOT to send it back to the seller. Why? First, the seller will simply send the camera back to the manufacturer as a “defective” unit. Most of the time there is not even a note that explains why the customer returned it. The manufacturer receives the unit, re-assesses it in a lab, and if it cannot find anything wrong with the camera (which it won’t in case of AF alignment issues), it will put it back on the market as a “refurbished” item. A returned item can never be sold as new again. So by sending it back to the seller, you are not notifying the manufacturer of the source of the problem. In addition, there is no guarantee that the replacement you receive will be in any way better. I know some people keep exchanging their purchases until they get a “good” sample. Well, some do it 5-6 times and never get a good one! I don’t think you would want to wait for weeks to get the issue resolved when it could be a matter of days for the manufacturer to address the problem. Also, by sending the item back to the seller, you are increasing the seller’s costs, since they put so much time and money to deal with defective products. It certainly also creates a lot of frustration for the seller to deal with these issues and they are obviously not to blame for manufacturer’s defects or QA issues.
So the best thing to do is to either send it to the manufacturer for repair / fine-tuning or try to calibrate the camera yourself (for advanced users, see my article on how to calibrate lenses). All manufacturers have support service centers that specifically deal with these issues and defects. Plus, this is the best way to force the manufacturer to improve its QA process. If more complaints come into service centers, the manufacturer could tighten up their QA thresholds to cut down its escalating costs.
Here is my recommended approach to handle this particular issue:
- Retain all sample images you have taken with the camera.
- Call the manufacturer’s service support number and explain in detail that you are having an autofocus problem with your camera. Provide the image samples to the support personnel and if they question your testing methodology, provide the URL to this article.
- Make sure to send both the camera and at least one lens for focus calibration. If you only have one camera and one lens then send both. If you have multiple lenses, send one or two lenses you had the least problems with before you bought the camera. Absolutely make sure to point out that you have no problems with lenses on other cameras so that they do not try to calibrate your lenses instead of the camera.
- Insist on making them pay for shipping and insurance if the product is under warranty. If the support person refuses to provide a paid shipping label, escalate the problem to the support manager. Why should you be paying for shipping a defective product in the first place?
Hope this helps! Please let me know if you have any questions!
Thank you. Worked great. My Nikon was factory refurbished. I was afraid I might have a focus issue, but the thoroughness of your test, proved I have a great camera. I didn’t read whether I needed to zoom in with a telephoto, so I did it both ways.
Your chart and tests wont open for printing a focus test.
I need Nikon and canon, sony lenses alignment tool for calibration
It’s highly unlikely Nikon tests any items they receive from the sellers, I had numerous issues with refurbished Nikon items, which were simply not functioning or severely damaged. I had decided to never buy any refurbished Nikon product. Even Nikon’s own 90 day refurbished product warranty clearly says they have very low confidence in them.
I have had excellent luck with Nikon “refurbished…”
I was hoping you could clarify two things.
1. Is it not recommended to conduct this test at or close to a lens’ suggested MFD (Minimum Focus Distance)? If not, why?
2. You state in the instructions that “The goal is to stand close enough to be able to have a shallow depth of field.” Is there a recommended minimum depth of field?
Just read the article and it makes things clear to this newbie! I am going to set up a test area and see how I make out. I always seem to get shots that are almost in perfect focus but lack a little bit to make them great. Thanks for all this info!
Very informative and useful article, Thank you for posting. When using auto iso in manual mode with external flash E-TTL II meter, my iso range is limited to a max of 400 iso. Is this a canon standard or my settings are not correct? I would like to have the option to chose the iso range instead of the camera limit of 400 iso. Your help would be much appreciated.
Laszlo
Great article. Thanks for taking the time to put this together.
I have calibrated my lenses. I understand why we should turn off the lens fine tuning when we capture the focus chart in Live View mode. But since my lenses are fine tuned should I turn it back on when I capture the second image without Live View? If I do not turn it on I know the images will not be in focus because they are not calibrated.
I have a D700 and was using , Angenieux 24-70 zoom. The autofocus will suddenly stop working and at times even the shutter release get frozen. if I remove the lens and re attach, the AF function will work again. but then again the same problem gets repeated. I have been setting the aperture to the smallest value. But when the AF stops working, the LCD screen shows the F 11…………..
Please help
vijay
i guess i have a different take than most. I’ve been shooting professionally for 25 years. raised my kids and bought my home on the proceeds. i need this equipment to work right out of the box. many thousands are on the line.
if canon knows they have (lets say) a 1 percent failure rate of their product out of the box they should address this. It should not in any way be the responsibility of the purchaser to deal with. They should have a built in program to immediately send a pre calibrated and tested lens to the consumer without question. one that is known to be correct because its been tested in their lab.
then they can then deal with their manufacturing defects correctly. believing that its the consumers job to identify and deal with their crappy QC is inexcusable. if these lenses are tested before leaving the manufacturer this wouldnt happen.
what ever happened to pride in your work ? I would never be able to send an out of focus shot to a client and “if they notice a problem” i might fix it at their expense. what a joke. who knows better than Canon wether the calibration is dead on. its their job to deal with it. NOT THE CONSUMER.
sure its unreasonable for a purchaser to expect every item to be perfect out of the box. but to have to deal with it after spending thousands is ridiculous. I own over 12k worth of canon gear and rely on it to feed my family. if i have a problem with calibration i expect it to be taken care with minimum hassle on my part.
they should send me an absolutely perfect brand new item if i have any concerns no questions asked. If they are making a quality product that policy should not affect their bottom line but enhance it. they should be embarrassed and apologetic about the mistake. NOT aloof and uncaring.
this is what happens when companies get too big. Im considering selling all my Canon stuff and buying a second medium format rig. WAY better IQ by the way. the thought of having to calibrate my 7 canon lenses and two Mark III bodies is worse than a nightmare. it should be right from the factory or made so with no effort on my part. They already have my money !
give me a break. Canon needs a better policy concerning quality issues. I know of other companies that would never treat a consumer that way…even if they are more rare every day.